Title: COVID-19 Coronavirus: Unraveling the Pandemic's Impact on Health, Society, and Global Dynamics
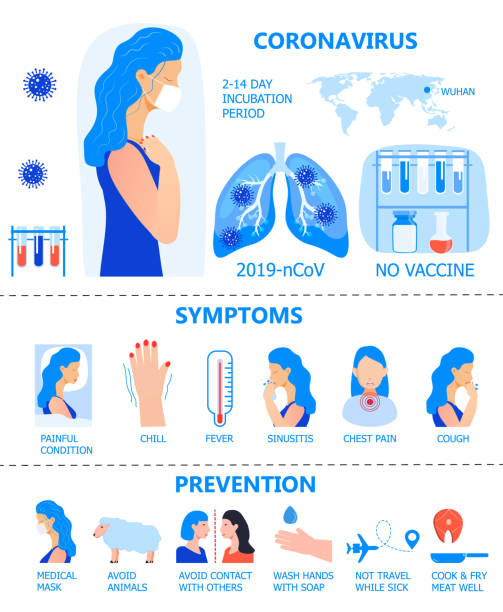
In late 2019, a novel coronavirus, now known as SARS-CoV-2, emerged in Wuhan, China, igniting a global health crisis that swiftly turned into a pandemic. The virus, responsible for the disease named COVID-19, spread with unprecedented speed, challenging healthcare systems, economies, and daily life across the world. This article delves into the multifaceted dimensions of the COVID-19 pandemic, exploring its origins, its impact on public health and society, the global response, and the lessons learned.
Origins and Spread:
SARS-CoV-2 is believed to have originated from bats and possibly transmitted to humans through an intermediate host. The first cases emerged in Wuhan, but the virus quickly crossed borders due to international travel, becoming a pandemic within months. The virus's transmission occurs primarily through respiratory droplets, leading to the implementation of public health measures such as mask mandates, social distancing, and lockdowns to mitigate its spread.
Impact on Public Health:
COVID-19's impact on public health has been profound. The virus has caused millions of deaths worldwide, with vulnerable populations like the elderly and those with preexisting conditions being the most affected. Healthcare systems faced immense pressure, grappling with shortages of medical supplies, hospital beds, and healthcare workers. Rapid vaccine development became a beacon of hope, leading to unprecedented collaborations between pharmaceutical companies, researchers, and governments.
Societal Disruption:
The pandemic's ripple effects extended beyond health systems. Lockdowns and restrictions led to disruptions in daily life, from remote work becoming the norm to the closure of schools, restaurants, and cultural venues. Mental health issues surged due to isolation, economic uncertainty, and fear of the virus. The digital divide became more pronounced as online access became crucial for work, education, and social interaction.
Economic Challenges:
Global economies faced severe challenges as businesses shuttered, supply chains faltered, and unemployment rates soared. Governments worldwide introduced stimulus packages to counter economic downturns, leading to debates about the best approaches for recovery. The pandemic underscored the need for resilient and adaptive economic systems.
Global Response and Cooperation:
The pandemic prompted both national and international responses. Countries implemented a variety of strategies, ranging from strict lockdowns to targeted testing and contact tracing. The World Health Organization (WHO) played a central role in providing guidance and coordinating global efforts. Despite some successes, the pandemic also highlighted disparities in the global response, with debates over vaccine distribution and access dominating discussions.
Scientific Breakthroughs:
The scientific community rallied to address the crisis. Researchers swiftly sequenced the virus's genome, enabling the rapid development of diagnostic tests and vaccines. Collaborative efforts led to the creation of multiple effective vaccines in record time, demonstrating the power of scientific innovation when faced with a global threat.
Vaccine Rollout and Hesitancy:
Vaccination campaigns emerged as a critical tool to control the pandemic's spread. However, vaccine rollout was marred by challenges such as production bottlenecks, distribution inequities, and vaccine hesitancy. Misinformation and skepticism fueled concerns, highlighting the importance of public health communication in fostering vaccine acceptance.
Lessons Learned and Future Preparedness:
The COVID-19 pandemic revealed shortcomings in global preparedness for health crises. It emphasized the need for robust healthcare infrastructure, international collaboration, and early warning systems. Governments and organizations must learn from this experience to be better equipped for future pandemics.
In conclusion, the COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, has had a far-reaching impact on every aspect of human life. Its origins, rapid spread, and devastating effects on health, society, and economies underscore the interconnectedness of our world. The pandemic highlighted both strengths and weaknesses in our global response and cooperation, revealing the importance of science, resilience, and preparedness in the face of unforeseen challenges. As vaccines continue to be distributed and the world adapts, the lessons learned from this crisis will shape our approach to future health crises and the way we build a more resilient, equitable, and interconnected world.
In late 2019, a novel coronavirus, now known as SARS-CoV-2, emerged in Wuhan, China, igniting a global health crisis that swiftly turned into a pandemic. The virus, responsible for the disease named COVID-19, spread with unprecedented speed, challenging healthcare systems, economies, and daily life across the world. This article delves into the multifaceted dimensions of the COVID-19 pandemic, exploring its origins, its impact on public health and society, the global response, and the lessons learned.
Origins and Spread:
SARS-CoV-2 is believed to have originated from bats and possibly transmitted to humans through an intermediate host. The first cases emerged in Wuhan, but the virus quickly crossed borders due to international travel, becoming a pandemic within months. The virus's transmission occurs primarily through respiratory droplets, leading to the implementation of public health measures such as mask mandates, social distancing, and lockdowns to mitigate its spread.
Impact on Public Health:
COVID-19's impact on public health has been profound. The virus has caused millions of deaths worldwide, with vulnerable populations like the elderly and those with preexisting conditions being the most affected. Healthcare systems faced immense pressure, grappling with shortages of medical supplies, hospital beds, and healthcare workers. Rapid vaccine development became a beacon of hope, leading to unprecedented collaborations between pharmaceutical companies, researchers, and governments.
Societal Disruption:
The pandemic's ripple effects extended beyond health systems. Lockdowns and restrictions led to disruptions in daily life, from remote work becoming the norm to the closure of schools, restaurants, and cultural venues. Mental health issues surged due to isolation, economic uncertainty, and fear of the virus. The digital divide became more pronounced as online access became crucial for work, education, and social interaction.
Economic Challenges:
Global economies faced severe challenges as businesses shuttered, supply chains faltered, and unemployment rates soared. Governments worldwide introduced stimulus packages to counter economic downturns, leading to debates about the best approaches for recovery. The pandemic underscored the need for resilient and adaptive economic systems.
Global Response and Cooperation:
The pandemic prompted both national and international responses. Countries implemented a variety of strategies, ranging from strict lockdowns to targeted testing and contact tracing. The World Health Organization (WHO) played a central role in providing guidance and coordinating global efforts. Despite some successes, the pandemic also highlighted disparities in the global response, with debates over vaccine distribution and access dominating discussions.
Scientific Breakthroughs:
The scientific community rallied to address the crisis. Researchers swiftly sequenced the virus's genome, enabling the rapid development of diagnostic tests and vaccines. Collaborative efforts led to the creation of multiple effective vaccines in record time, demonstrating the power of scientific innovation when faced with a global threat.
Vaccine Rollout and Hesitancy:
Vaccination campaigns emerged as a critical tool to control the pandemic's spread. However, vaccine rollout was marred by challenges such as production bottlenecks, distribution inequities, and vaccine hesitancy. Misinformation and skepticism fueled concerns, highlighting the importance of public health communication in fostering vaccine acceptance.
Lessons Learned and Future Preparedness:
The COVID-19 pandemic revealed shortcomings in global preparedness for health crises. It emphasized the need for robust healthcare infrastructure, international collaboration, and early warning systems. Governments and organizations must learn from this experience to be better equipped for future pandemics.
In conclusion, the COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, has had a far-reaching impact on every aspect of human life. Its origins, rapid spread, and devastating effects on health, society, and economies underscore the interconnectedness of our world. The pandemic highlighted both strengths and weaknesses in our global response and cooperation, revealing the importance of science, resilience, and preparedness in the face of unforeseen challenges. As vaccines continue to be distributed and the world adapts, the lessons learned from this crisis will shape our approach to future health crises and the way we build a more resilient, equitable, and interconnected world.