Title: Understanding the Impact and Management of Coronavirus Hospitalizations
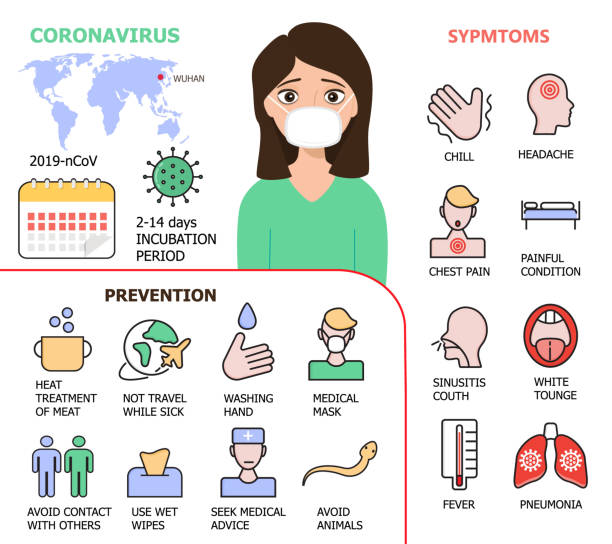
In late 2019, a novel coronavirus emerged in the city of Wuhan, China, setting off a global pandemic. The virus, known as SARS-CoV-2, causes the disease COVID-19 and has since spread to nearly every corner of the world. While the majority of COVID-19 cases result in mild to moderate symptoms, a significant portion of individuals experience severe illness that requires hospitalization. This article delves into the complexities of coronavirus hospitalizations, exploring their impact on healthcare systems, the factors contributing to severe cases, and the strategies employed for effective management.
The Magnitude of the Issue:
Coronavirus hospitalizations have put immense strain on healthcare systems worldwide. Overcrowded hospitals, shortage of medical supplies, and exhausted healthcare workers have become unfortunate hallmarks of this pandemic. Hospitals in various countries have been pushed to their limits, prompting the rapid construction of temporary facilities and the implementation of surge plans to accommodate the overwhelming number of patients.
Factors Contributing to Severe Cases:
Several factors contribute to the severity of COVID-19 cases, leading to hospitalizations. Age is a significant determinant, with older individuals being more susceptible to severe illness. Underlying health conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and compromised immune systems also increase the risk of severe COVID-19. Additionally, social determinants of health, such as access to healthcare, living conditions, and socioeconomic status, play a role in determining the severity of cases.
Challenges in Management:
Managing coronavirus hospitalizations presents a unique set of challenges. The unpredictable nature of the disease and the potential for sudden deterioration in patient condition require vigilant monitoring and prompt medical interventions. Hospital resources, including ventilators, oxygen supply, and ICU beds, can become scarce during surges in cases. Healthcare professionals are not only tasked with medical care but also face emotional and psychological strain as they witness the toll of the pandemic on patients and their families.
Medical Interventions and Treatments:
Treatment strategies for hospitalized COVID-19 patients have evolved over time as our understanding of the disease has deepened. Early in the pandemic, antimalarial drugs and antivirals were considered as potential treatments, but their effectiveness was limited. As of the latest knowledge, the use of corticosteroids, anticoagulants, and monoclonal antibodies has shown promise in reducing the severity of the disease and improving patient outcomes. Vaccination campaigns have also played a crucial role in reducing the number of severe cases and hospitalizations.
The Importance of Prevention:
Preventing the spread of SARS-CoV-2 remains the most effective strategy to reduce the burden of coronavirus hospitalizations. Public health measures such as mask mandates, social distancing, hand hygiene, and travel restrictions have been instrumental in controlling the transmission of the virus. Vaccination, too, has proven to be a game-changer, not only in preventing severe illness but also in curbing hospitalizations.
The Road Ahead:
While vaccination efforts have provided a glimmer of hope, the road to recovery is not without challenges. Variants of the virus continue to emerge, some of which may evade immunity and impact the severity of illness. Ongoing research is crucial to understanding these variants and adapting strategies accordingly. Investments in healthcare infrastructure and preparedness are also essential to ensure that healthcare systems can better withstand future crises.
Conclusion:
Coronavirus hospitalizations have placed an unprecedented burden on healthcare systems and exposed vulnerabilities in public health preparedness. The pandemic has reinforced the importance of international collaboration, timely research, and proactive healthcare planning. As we continue to battle the challenges posed by COVID-19, a holistic approach encompassing prevention, treatment, and infrastructure development is paramount to effectively manage and mitigate the impact of coronavirus hospitalizations.
In late 2019, a novel coronavirus emerged in the city of Wuhan, China, setting off a global pandemic. The virus, known as SARS-CoV-2, causes the disease COVID-19 and has since spread to nearly every corner of the world. While the majority of COVID-19 cases result in mild to moderate symptoms, a significant portion of individuals experience severe illness that requires hospitalization. This article delves into the complexities of coronavirus hospitalizations, exploring their impact on healthcare systems, the factors contributing to severe cases, and the strategies employed for effective management.
The Magnitude of the Issue:
Coronavirus hospitalizations have put immense strain on healthcare systems worldwide. Overcrowded hospitals, shortage of medical supplies, and exhausted healthcare workers have become unfortunate hallmarks of this pandemic. Hospitals in various countries have been pushed to their limits, prompting the rapid construction of temporary facilities and the implementation of surge plans to accommodate the overwhelming number of patients.
Factors Contributing to Severe Cases:
Several factors contribute to the severity of COVID-19 cases, leading to hospitalizations. Age is a significant determinant, with older individuals being more susceptible to severe illness. Underlying health conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and compromised immune systems also increase the risk of severe COVID-19. Additionally, social determinants of health, such as access to healthcare, living conditions, and socioeconomic status, play a role in determining the severity of cases.
Challenges in Management:
Managing coronavirus hospitalizations presents a unique set of challenges. The unpredictable nature of the disease and the potential for sudden deterioration in patient condition require vigilant monitoring and prompt medical interventions. Hospital resources, including ventilators, oxygen supply, and ICU beds, can become scarce during surges in cases. Healthcare professionals are not only tasked with medical care but also face emotional and psychological strain as they witness the toll of the pandemic on patients and their families.
Medical Interventions and Treatments:
Treatment strategies for hospitalized COVID-19 patients have evolved over time as our understanding of the disease has deepened. Early in the pandemic, antimalarial drugs and antivirals were considered as potential treatments, but their effectiveness was limited. As of the latest knowledge, the use of corticosteroids, anticoagulants, and monoclonal antibodies has shown promise in reducing the severity of the disease and improving patient outcomes. Vaccination campaigns have also played a crucial role in reducing the number of severe cases and hospitalizations.
The Importance of Prevention:
Preventing the spread of SARS-CoV-2 remains the most effective strategy to reduce the burden of coronavirus hospitalizations. Public health measures such as mask mandates, social distancing, hand hygiene, and travel restrictions have been instrumental in controlling the transmission of the virus. Vaccination, too, has proven to be a game-changer, not only in preventing severe illness but also in curbing hospitalizations.
The Road Ahead:
While vaccination efforts have provided a glimmer of hope, the road to recovery is not without challenges. Variants of the virus continue to emerge, some of which may evade immunity and impact the severity of illness. Ongoing research is crucial to understanding these variants and adapting strategies accordingly. Investments in healthcare infrastructure and preparedness are also essential to ensure that healthcare systems can better withstand future crises.
Conclusion:
Coronavirus hospitalizations have placed an unprecedented burden on healthcare systems and exposed vulnerabilities in public health preparedness. The pandemic has reinforced the importance of international collaboration, timely research, and proactive healthcare planning. As we continue to battle the challenges posed by COVID-19, a holistic approach encompassing prevention, treatment, and infrastructure development is paramount to effectively manage and mitigate the impact of coronavirus hospitalizations.