Title: Understanding Coronavirus (COVID-19): A Comprehensive Overview
In December 2019, a novel coronavirus emerged in the city of Wuhan, China, setting off a global pandemic that would reshape the way we live, work, and interact. Named SARS-CoV-2, this virus caused the disease known as COVID-19, which rapidly spread across the world, challenging healthcare systems, economies, and societies at large. This comprehensive overview delves into the origins, transmission, symptoms, prevention, and global response to the coronavirus pandemic.
Origins and Transmission:
Coronaviruses are a family of viruses that can infect both animals and humans. SARS-CoV-2 is believed to have originated in bats and possibly transmitted to humans through an intermediate animal host, possibly a seafood market in Wuhan. Human-to-human transmission occurs primarily through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs, sneezes, talks, or even breathes. The virus can also survive on surfaces for varying durations, contributing to its spread.
Symptoms and Severity:
COVID-19 presents a wide range of symptoms, from mild to severe. Common symptoms include fever, cough, shortness of breath, fatigue, muscle or body aches, loss of taste or smell, sore throat, and headache. Severe cases can lead to pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), organ failure, and even death, especially among older adults and individuals with underlying health conditions.
Preventive Measures:
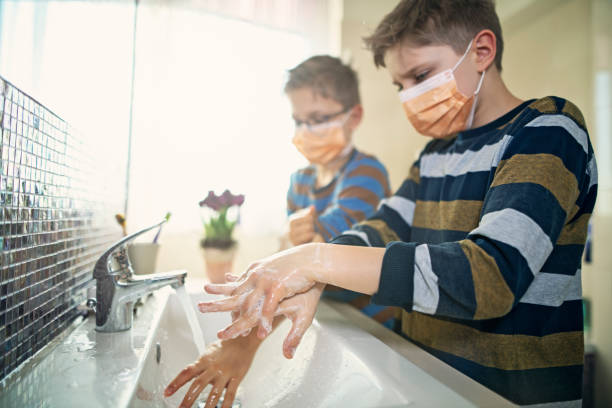
To curb the spread of the virus, health organizations and governments recommended several preventive measures. These include wearing face masks, practicing physical distancing, frequent handwashing with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, and using hand sanitizers when soap is not available. Lockdowns, travel restrictions, and quarantine measures were also implemented to limit contact between individuals and reduce the transmission rate.
Global Response:
Governments worldwide mobilized efforts to manage the pandemic's impact. Testing and contact tracing became critical tools in identifying and isolating cases. Healthcare systems faced unprecedented challenges due to the surge in cases, leading to shortages of medical supplies and overwhelmed hospitals in some areas. Researchers raced to develop treatments and vaccines, with several vaccines eventually receiving emergency use authorization to control the spread of the virus.
Vaccine Development and Distribution:
The rapid development of COVID-19 vaccines marked a remarkable achievement in medical science. Multiple vaccines, such as those developed by Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, AstraZeneca, and Johnson & Johnson, demonstrated high efficacy in clinical trials. Vaccination campaigns were launched globally to achieve herd immunity and reduce the virus's impact. However, challenges related to vaccine distribution, hesitancy, and equitable access persisted.
Economic and Social Impact:
The pandemic led to significant economic disruptions as businesses shuttered, unemployment rates soared, and supply chains faltered. Remote work and online education became the norm, reshaping how societies functioned. The pandemic also exacerbated existing inequalities, disproportionately affecting vulnerable populations and straining healthcare systems in lower-income countries.
Mental Health and Well-being:
The isolation, uncertainty, and fear brought about by the pandemic took a toll on mental health worldwide. Lockdowns and social distancing measures led to increased feelings of loneliness, anxiety, and depression. Access to mental health services and strategies for coping with these challenges became crucial aspects of the pandemic response.
The Road to Recovery:
As vaccination efforts expanded, many regions experienced periods of lower case numbers and eased restrictions. However, new variants of the virus raised concerns about their potential impact on vaccine efficacy and transmissibility. Continued vigilance through testing, vaccination, and adherence to preventive measures remained vital in the ongoing battle against COVID-19.
Conclusion:
The COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated the interconnectedness of our world and the importance of a coordinated global response to public health crises. While strides have been made in understanding and combating the virus, challenges such as vaccine distribution, variant management, and long-term societal adjustments persist. As we move forward, the lessons learned from this pandemic will undoubtedly shape our approach to healthcare, preparedness, and collaboration on a global scale.
In December 2019, a novel coronavirus emerged in the city of Wuhan, China, setting off a global pandemic that would reshape the way we live, work, and interact. Named SARS-CoV-2, this virus caused the disease known as COVID-19, which rapidly spread across the world, challenging healthcare systems, economies, and societies at large. This comprehensive overview delves into the origins, transmission, symptoms, prevention, and global response to the coronavirus pandemic.
Origins and Transmission:
Coronaviruses are a family of viruses that can infect both animals and humans. SARS-CoV-2 is believed to have originated in bats and possibly transmitted to humans through an intermediate animal host, possibly a seafood market in Wuhan. Human-to-human transmission occurs primarily through respiratory droplets when an infected person coughs, sneezes, talks, or even breathes. The virus can also survive on surfaces for varying durations, contributing to its spread.
Symptoms and Severity:
COVID-19 presents a wide range of symptoms, from mild to severe. Common symptoms include fever, cough, shortness of breath, fatigue, muscle or body aches, loss of taste or smell, sore throat, and headache. Severe cases can lead to pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), organ failure, and even death, especially among older adults and individuals with underlying health conditions.
Preventive Measures:
To curb the spread of the virus, health organizations and governments recommended several preventive measures. These include wearing face masks, practicing physical distancing, frequent handwashing with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, and using hand sanitizers when soap is not available. Lockdowns, travel restrictions, and quarantine measures were also implemented to limit contact between individuals and reduce the transmission rate.
Global Response:
Governments worldwide mobilized efforts to manage the pandemic's impact. Testing and contact tracing became critical tools in identifying and isolating cases. Healthcare systems faced unprecedented challenges due to the surge in cases, leading to shortages of medical supplies and overwhelmed hospitals in some areas. Researchers raced to develop treatments and vaccines, with several vaccines eventually receiving emergency use authorization to control the spread of the virus.
Vaccine Development and Distribution:
The rapid development of COVID-19 vaccines marked a remarkable achievement in medical science. Multiple vaccines, such as those developed by Pfizer-BioNTech, Moderna, AstraZeneca, and Johnson & Johnson, demonstrated high efficacy in clinical trials. Vaccination campaigns were launched globally to achieve herd immunity and reduce the virus's impact. However, challenges related to vaccine distribution, hesitancy, and equitable access persisted.
Economic and Social Impact:
The pandemic led to significant economic disruptions as businesses shuttered, unemployment rates soared, and supply chains faltered. Remote work and online education became the norm, reshaping how societies functioned. The pandemic also exacerbated existing inequalities, disproportionately affecting vulnerable populations and straining healthcare systems in lower-income countries.
Mental Health and Well-being:
The isolation, uncertainty, and fear brought about by the pandemic took a toll on mental health worldwide. Lockdowns and social distancing measures led to increased feelings of loneliness, anxiety, and depression. Access to mental health services and strategies for coping with these challenges became crucial aspects of the pandemic response.
The Road to Recovery:
As vaccination efforts expanded, many regions experienced periods of lower case numbers and eased restrictions. However, new variants of the virus raised concerns about their potential impact on vaccine efficacy and transmissibility. Continued vigilance through testing, vaccination, and adherence to preventive measures remained vital in the ongoing battle against COVID-19.
Conclusion:
The COVID-19 pandemic demonstrated the interconnectedness of our world and the importance of a coordinated global response to public health crises. While strides have been made in understanding and combating the virus, challenges such as vaccine distribution, variant management, and long-term societal adjustments persist. As we move forward, the lessons learned from this pandemic will undoubtedly shape our approach to healthcare, preparedness, and collaboration on a global scale.